Introduction
The
scientific techniques used to measure the memory system is known as method of
studying memory. Memory can be measured in various ways. As we know that memory
is of different types, hence for measurement of specific type of memory specific
method is required. Hermann Ebbinghaus (1885), German psychologist who first
systematically studied memory. He used recall method and suggested that
retention can be tested either by immediate recall or delayed recall.
Important
Methods of Studying Memory
(i) Recall method (for measuring facts) – The
repetition of learned material after specific lapse of time is called recall.
The recall of learned material depends upon individual and stimulus related
factors. The interesting, meaningful and short learning material is easy to
memorize and recall.
Recall is
of two type i.e.
(a) Free
Recall
(b) Serial
Recall
(a) Free
recall – In this method, participants are presented with some words [preferably meaningless] or
information which they are asked to memorize and recall [after some time] in any order.
(b) Serial
Recall – The administration method is similar to the free recall method, the only difference is that
participants are required to recall the learned material in the same order as it was presented.
(ii) Recognition (Episodic memory) – According
to Guilford (1917) recognition is knowing again the same material. In
recognition, participants are shown learning material along with distracter
items (the material that they had not seen earlier) and asked to memorize. Then
they are asked to recognize the learned [stimuli] items. The % of recognition
can be calculated by the following formula: -
% of Recognition =
R= total no. correct items recognized.
W= total no. items incorrectly recognized.
K= total no. of distractors presented [during learning
+ during recognition].
n= no. of items presented for learning.
For example – A
participant could correctly recognize 6 items out of 10. The experimenter presented 10 distractions
during learning phase while 10 different distractors during recognition phase.
Then calculate the % of recognition.
Answer: % of Recognition = 6 –
4/19 x 10 = 57.89%
(iii) Sentence Verification Method (for
measuring semantic memory) – Semantic memory by virtue of its nature [general
knowledge] is not prone to forgetting. In this method the participants are
asked to indicate whether the given sentences are true or false. Faster the
participants’ correct response better is the semantic memory i.e. the better is
the retained information which is needed to verify the shown sentences.
(iv) Priming (for measuring information we cannot report verbally) – In this
method, participants are shown a list of meaningful words, such as truck,
machine etc. and then they are shown parts of these words tru, mac along with
parts of other meaningful words which they had not seen earlier. Then
participants are asked to complete the words. It has been found that
participants complete parts of seen words more quickly than parts of words they
had not seen. When asked, they are often unaware of this and report that they
have only guessed (NCERT).
(v) Relearning – This
method was suggested by Ebbinghaus (1885) and also known as method of ‘saving’.
The quantitative capacity of memory is measured with the help of this method.
The participants are provided with learning material. Then they are asked to
memorize it fully. After specific time interval the same material is presented
for memorizing. Time and number to trials taken by each participant is recorded
in both the situations.
Then percentage of saving [time and trials] is
calculated using following formula: -
Saving % =
OLT = Original learning trials
RLT = Relearning trials
For example – if a participant takes 20 trials to
memorize a original material and 8 trials to relearn it then % of saving will
be
Saving % = (20-18/20)100 = 60%
(v) Reconstruction – In this
method the participants are presented with a set of stimuli in pre-decided
arrangement. Then the arrangement of the set of stimuli is disturbed and
presented to the participant to arrange it in the order shown earlier. Time
taken to reconstruct or arrange the stimulus is recorded.
References:
1. NCERT,
XI Psychology Text book.
2. http://www.preservearticles.com/psychology/methods-used-for-the-measurement-of-human-memory/3926.
*******
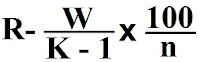





No comments:
Post a Comment